|
| Regulation of the epithelial permeability by tight junctions. |
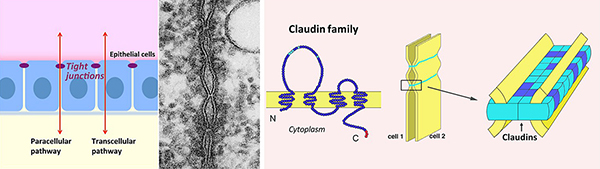
Claudins are the membrane proteins that constitute the core structure of tight junctions and determine their barrier/channel properties. Claudin family comprise more than twenty members. Cell biological and physiological analyses have clarified that 1) multiple claudin subtypes are co-expressed in most epithelial cells, 2) claudin combinations are unique for individual epithelial cell types, 3) each claudin has its unique barrier/channel property. Those characteristics of claudins creates functional diversity of tight junctions depending on physiological requirement of each epithelial type. To date, many studies on physiological significance of tight junctions and disorders caused by impaired tight junction function have been reported by analyzing various claudin deficient mice and human claudin mutations. These studies have clarified that tight junctions play crucial roles not only as strong barriers, but also as channels that permit the leak of electrolytes through the paracellular pathway for proper epithelial transport cooperated with the transcellular transport system.
To investigate such interesting aspects of tight junctions in more detail, cultured epithelial cell models in which a given combination of claudins are reconstituted are useful. However, one big problem is that the established cultured epithelial cell lines express many claudin types as background. This prohibits us from analyzing tight junctions bearing a claudin combination that mimics a given epithelial type in a certain organ by using cultured epithelial cells. To overcome this problem, we are trying to generate claudin-deficient epithelial cells via genome editing. Once such a cell line is established, we can analyze the function of tight junctions generated by single claudin subtype or by given combinations of claudin subtypes. We believe that this approach will provide the next breakthrough in this research field.
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|

|
|
| 1. |
Otani T, Furuse M. Tight junction structure and function revisited. (2020) Trends Cell Biol. S0962-8924(20)30151-3. Review |
| 2. |
Otani T, Nguyen TP, Tokuda S, Sugihara K, Sugawara T, Furuse K, Miura T, Ebnet K, Furuse M. (2019) Claudins and JAM-A coordinately regulate tight junction formation and epithelial polarity. J Cell Biol. 218:3372-3396. |
| 3. |
Tokuda S, Furuse M. (2015) Claudin-2 Knockout by TALEN-Mediated Gene Targeting in MDCK Cells: Claudin-2 Independently Determines the Leaky Property of Tight Junctions in MDCK Cells. PLoS One. 10:e0119869. |
|
|
 |
|
Copyright(C) 2017- NIPS Division of Cell Stracture. All rights reserved.
Last modified: 2022-08-10 |