The present study examined infants' brain activity in response to upright and inverted faces using near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), which can non-invasively record hemodynamic changes of the brain. NIRS is particularly useful for recording in infants, since recordings can be made, even while the infants are awake, without fixing their body and brain. For this objective, we used newly developed sensor probes of NIRS for recording in infants. We measured changes in cerebral oxygenation in 10 5-8-month-olds' left and right lateral areas while they were looking at upright and inverted faces. The results are summarized as follows: (1) the concentration of oxyhemoglobin (oxy-Hb) and total hemoglobin (total-Hb) increased significantly in the right lateral area during the upright face condition, (2) the concentration of total-Hb in the right lateral area differed significantly between the upright and inverted conditions, (3) hemodynamic changes were maximal in the temporal region, probably in the superior temporal sulcus (STS) in both hemispheres, and (4) the right hemisphere seems to be more important for recognizing upright faces. This is the first evidence showing that there is an inter-hemispheric difference on the effect of face inversion in the infant brain using a hemodynamic method.
Otsuka Y, Nakato E, Kanazawa S, Yamaguchi MK, Watanabe S, Kakigi R: Neural activation to upright and inverted faces in infants measured by near infrared spectroscopy. Neuroimage. 34(1):399-406, 2007
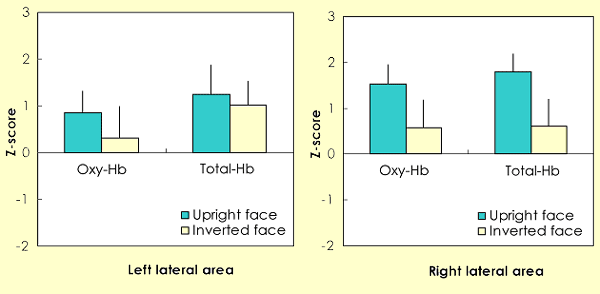
The average change of the oxy-Hb and total-Hb concentrations during the presentation of the upright and inverted faces. Data from 24 channels were averaged over 10 infants within left and right hemisphere. The left graphs show data from the left lateral area (1-12 channels), and the right graphs show data from the right lateral area (13-24 channels). The vertical bar in the graphs represents 1 standard error (SE). The concentration of both oxy-Hb and total-Hb in the right lateral area was significantly greater than the chance level of 0 in the upright face condition (p < .01). Moreover, the concentration of total-Hb in the right lateral area differed significantly between the upright and inverted conditions ( p < .05). No such difference was observed in the left lateral area.