We created the FAST (Flexible Accelerated STOP TetO-knockin) system, an efficient method for manipulating gene expression in vivo to rapidly screen animal models of disease. A single gene targeting event yields 2 distinct knockin mice -STOP-tetO and tetO knockin¬- which permit generation of multiple strains with variable expression patterns: 1) knockout, 2) Cre-mediated rescue; 3) tTAmediated misexpression; 4) tTA-mediated overexpression; and 5) tTS-mediated conditional knockout/knockdown. Using the FAST system, multiple gain- and loss-of-function strains can therefore be generated on a timescale not previously achievable. These strains can then be screened for clinically-relevant abnormalities. We demonstrate the flexibility and broad applicability of the FAST system by targeting several genes encoding proteins implicated in neuropsychiatric disorders: Mlc1, Neuroligin 3, the serotonin 1A receptor, and the serotonin 1B receptor.
Kenji F Tanaka, Susanne E Ahmari, E D Leonardo, Jesse W Richardson-Jones, Elaine C Budreck, Peter Scheiffele, Shouta Sugio, Naoko Inamura, Kazuhiro Ikenaka, Rene Hen Biological Psychiatry Volume 67, Issue 8, Pages xxx-yyy (15 April 2010)
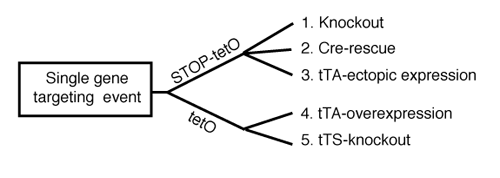
Single gene targeting event yields two distinct knock-in mice (STOP-tetO and tetO), which ultimately provide 5 different applications.
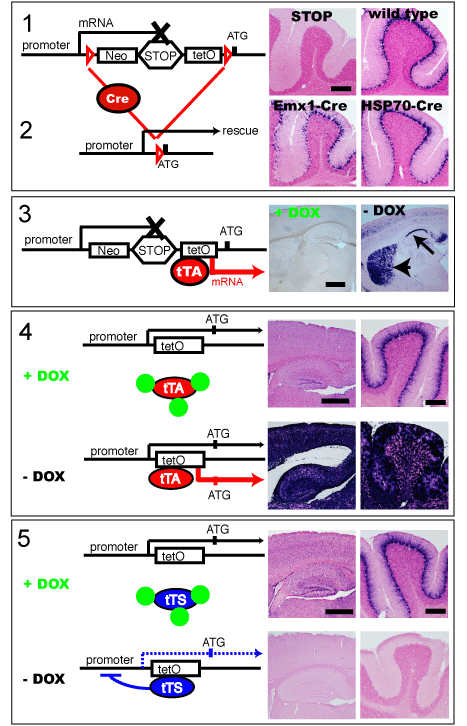
(1) STOP-tetO knock in mice are indistinguishable from straight null mice. STOP cassette terminates transcription. Images show Mlc1 ISH in the cerebellar lobe of STOP-tetO homozygote and wild type mice. Note that Mlc1 mRNA is expressed in astrocyte lineage cells.
(2) Cre-mediated rescue. Cre protein excises loxP flanking STOP-tetO cassette, and transcription is rescued. Mlc1 ISH of Emx1-Cre::Mlc1 STOP-tetO and HSP70-Cre::Mlc1 STOP-tetO homozygote are shown.
(3) tTA-mediated ectopic expression tTA protein binds tetO sequence and transactivation occurs in DOX dependent manner (DOX-, DOX+). Neuronal Mlc1 mRNA induction were observed in αCamKII-tTA::Mlc1 STOP-tetO homozygote.
(4) tTA-mediated overexpression tetO knock in mice are indistinguishable from wild type mice. In the presence of doxycycline, tTA and tTS cannnot bind tetO site, and the level of Mlc1 expression is same as that of wild type mice. Pictures show Mlc1 ISH in cerebral cortex and cerebellum. Without DOX in Mlc1-mtTA::Mlc1 tetO homozygotes, tTA transactivates Mlc1 mRNA in addition to transcription driven by the endogenous promoter .
(5) tTS-mediated knockout
Without DOX, tTS surpresses transcription in Actin-tTS::Mlc1 tetO homozygote .