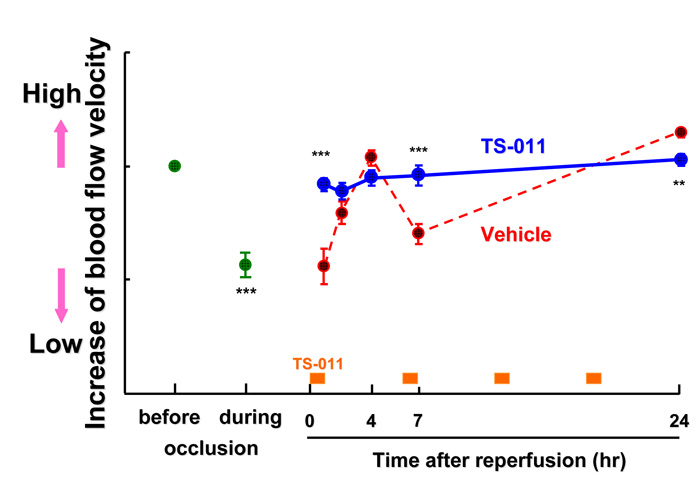
The inhibitor of 20-HETE synthesis, TS-011, improves cerebral microcirculatory autoregulation impaired by middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice.
Marumo T, Eto K, Wake H, Omura T, Nabekura J.
Br J Pharmacol (2010) 161:1391-1402
The microcirculation in the penumbra is an important target in the treatment of cerebral ischemia. In this study, we made a novel method to detect the brain microvascular dynamics in the penumbra in vivo using two-photon laser-scanning microscopy, and examined the effect of 20-HETE synthesis inhibitor, TS-011, on the damaged microvascular induced by ischemic insult. The cerebral microcirculatory autoregulation was impaired by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in mice, and microcirculations in penumbra were varied for 24 hours. In the MCAO mice injected with TS-011, the microcirculations in the penumbra were maintained at a control level. TS-011 also reduced the infarct volume in MCAO mice. TS-011 may show the neuroprotective effect through the improvement of the vasocontraction of microvessels induced by 20-HETE. The novel method we made in this study is the suitable one for detecting the changes in blood flows in many and same microvessels.
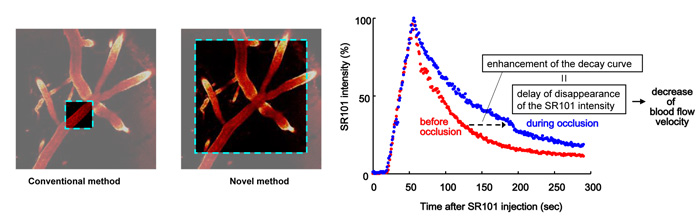
With our novel method, we can detect the blood flow in many microvessels, whereas conventional method (line scan) measures in each vessel. The sulforhodamine 101 (SR101) was injected into the jugular vein, and time-dependent changes in SR101 intensity were obtained by two-photon laser-scanning microscopy. The decay curve after the peak represents the disappearance of the SR101 intensity. The blood flow velocity was defined as the velocity of the disappearance of the SR101 intensity. Using this method, we could measure the blood flow velocity of many and same microvessels in the penumbra, and also we could estimate the effect of TS-011.