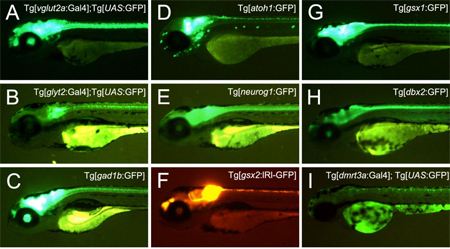
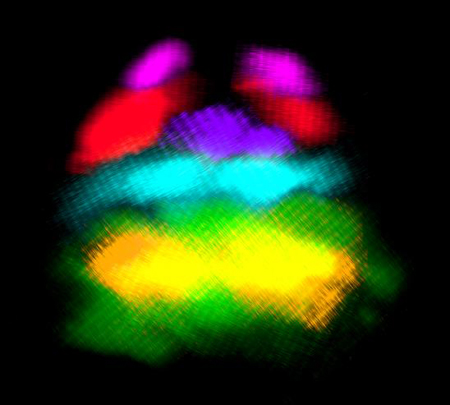
The developing nervous system consists of a variety of cell types. Transgenic animals expressing reporter genes in specific classes of neuronal cells are powerful tools for the study of neuronal network formation. We generated a wide variety of transgenic zebrafish that expressed reporter genes in specific classes of neurons or neuronal progenitors. These include lines in which neurons of specific neurotransmitter phenotypes expressed fluorescent proteins or Gal4, and lines in which specific subsets of the dorsal progenitor domain in the spinal cord expressed fluorescent proteins. Using these, we examined domain organization in the developing dorsal spinal cord, and found that there are six progenitor domains in zebrafish, which is similar to mice. We also systematically characterized neurotransmitter properties of neurons that are produced from each domain. These results form the basis for in-depth analyses of the neurons produced by each domain. In addition, given that reporter gene expressions occurs in a wide area of the nervous system in the lines generated, the transgenic fish should serve as powerful tools for the investigation of neuronal structures and functions in many regions of the nervous system.
本研究成果は、科学誌Developmentに発表された。
http://dev.biologists.org/content/early/2013/08/14/dev.099531.long
Satou, C., Kimura, Y., Hirata, H., Suster, M.L, Kawakami, K., and Higashijima, S. (2013). "Transgenic tools to characterize neuronal properties of discrete populations of zebrafish neurons." Development 140, 3927-3931.