大脳皮質機能研究系 大脳神経回路論研究部門
Morishima M, Kawaguchi Y (2006) Recurrent connection patterns of corticostriatal pyramidal cells in frontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 26, 4394-4405.
| 大脳基底核への皮質出力細胞の多様性とシナプス結合特異性 |
|
大脳皮質機能研究系 大脳神経回路論研究部門
|
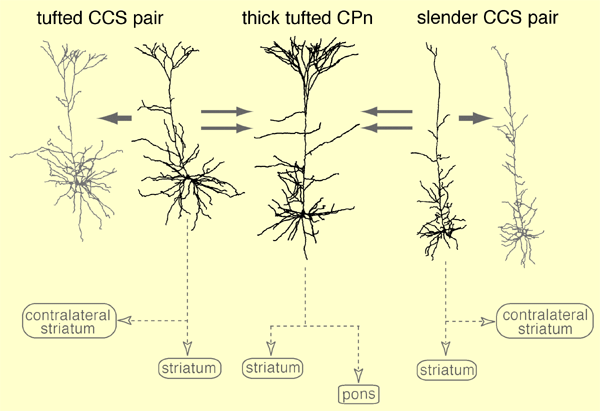
| 大脳皮質の構造に関して、最近、それを構成している細胞の種類がようやくわかり始めたところで、機能的回路の構築ルールの多くはまだほとんどわかっていません。大脳皮質、特に前頭皮質の多くの細胞が大脳基底核に信号を送ります。基底核の内部回路は、パーキンソン病に伴う神経変性の原因部位である事から比較的研究が進んでいますが、それに比べると、基底核へ信号を送り出す前頭皮質の神経回路の詳細については、今まで全く調べられていませんでした。今回、大脳基底核に投射すると考えられる二種類の錐体細胞を逆行性標識法により前頭皮質で確認し、その形態的な特徴とそれらの間のシナプス結合の様式を調べました。その結果、樹状突起の形態が両者で大きく異なるだけでなく、同じ種類の錐体細胞でも存在する皮質内の深さ方向に依存して形態が異なること、二種類の細胞の結合には方向選択性・細胞表面領域選択性があることがわかりました。これら2種類の錐体細胞から出る軸索は、基底核内でそれぞれ機能的役割が異なる神経細胞にシナプスを作ることが報告されています。それと合わせて考えると、大脳皮質の中で既に基底核内部回路の多様性に対応した神経分化が生じており、この異なる二種類の錐体細胞間の結合には階層性があることが明らかになりました。 Morishima M, Kawaguchi Y (2006) Recurrent connection patterns of corticostriatal pyramidal cells in frontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 26, 4394-4405. |
 |
| 橋核に軸索を伸ばす錐体細胞(CPn細胞)と両側の線条体にいくもの(CCS細胞)では、形態やシナプス結合様式が異なっていた。大脳基底核の内部回路の多様性に対応して、皮質の錐体細胞も分化していると考えられる。 |
| Corticostriatal pyramidal cells are heterogeneous in the frontal cortex. Here we show that subpopulations of corticostriatal neurons in the rat frontal cortex are selectively connected with each other based on their subcortical targets. Using paired recordings of retrogradely labeled cells, we investigated the synaptic connectivity between two projection cell types: (1) those projecting to the pons (corticopontine cell, CPn cell), often with collaterals to the striatum, and (2) those projecting to both sides of the striatum, but not to the pons (crossed corticostriatal cell, CCS cell). The two types were morphologically differentiated in regard to their apical tufts. The dendritic morphologies of CCS cells were correlated with their somatic depth within the cortex. CCS cells had reciprocal synaptic connections with each other and also provided synaptic input to CPn cells. However, connections from CPn to CCS cells were rarely found, even in pairs showing CCS to CPn connectivity. Further, CCS cells preferentially innervated the basal dendrites of other CCS cells but made contacts onto both the basal and apical dendrites of CPn cells. The amplitude of synaptic responses was to some extent correlated with the contact site number. Ratios of the EPSC amplitude to the contact number tended to be larger in the CCS to CCS connection. Therefore, our data demonstrate that these two types of corticostriatal cell distinct in their dendritic morphologies show directional and domain-dependent preferences in their synaptic connectivity. |