Identification of genes important for rat germ cell formation
2025.08.22
Research
Summary
Primordial germ cells (PGCs) are important precursor cells for sperm and eggs, but the genes involved in their formation in rats were previously unknown. The research group successfully identified the genes necessary for the formation of PGCs in rats. Furthermore, using PGCs created with these genes, the researchers produced healthy baby rats. These results have been published in the academic journal Stem Cell Reports.Result
Primordial germ cells (PGCs), the precursors of sperm and eggs, are generated during early embryo development. However, the genes involved in PGC specification in rats are not well understood. In this study, the research group used a previously developed method to induce rat PGCs from embryonic stem (ES) cells (*1) in vitro (Oikawa et al., 2022). By utilizing this system with candidate genes instead of a cytokine, BMP, they identified the key genes required for PGC specification.
In mice (*2), several important genes for PGC formation have been identified. The research group first tested whether these genes also function in rats. The results showed that the gene Tbxt could induce PGCs in rats, as it does in mice. However, the combination of three genes —Prdm14, Blimp1, and Tfap2c— that efficiently produce PGCs in mice, was insufficient in rats. The study revealed that additional proteins, Activin and WNT, were necessary. They found that the protein activated the gene Etv4, and the combination of these three genes with Etv4 successfully induced rat PGCs without the use of cytokines (Image). When these gene-induced PGCs were transplanted into sterile rat testes, they produced sperm cells capable of generating rat offspring via intracytoplasmic sperm injection (*3). This suggests that gene-induced PGCs are highly similar to naturally formed PGCs in early embryo development.
In summary, this study identified the genes necessary for rat PGC specification and underscored the importance of validating findings in mice using a rat model. Such research is expected to contribute to understanding infertility and the development of new reproductive technologies.
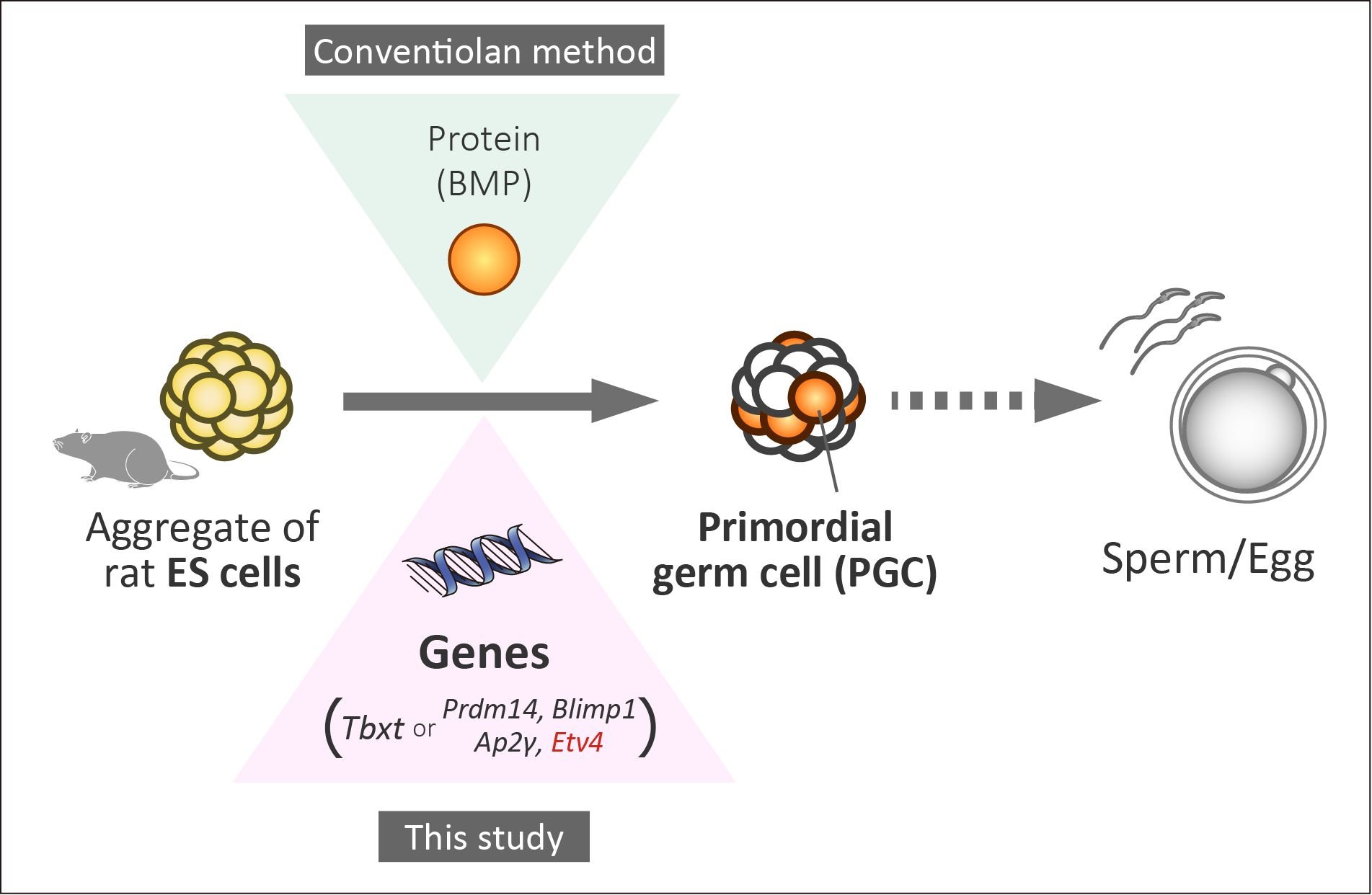
Schematics of this study
(References)
Oikawa, M., Kobayashi, H., Sanbo, M., Mizuno, N., Iwatsuki, K., Takashima, T., Yamauchi, K., Yoshida, F., Yamamoto, T., Shinohara, T., et al. (2022). Functional primordial germ cell-like cells from pluripotent stem cells in rats. Science. 376, 176-179.
Keywords
※1 ES cells (Embryonic Stem cells): Cells made from fertilized eggs that can turn into any type of cell in the body. They can also keep growing indefinitely in a lab dish.
※2 Mouse and Rat: A mouse is a small house mouse, and a rat is a larger Norway rat. Both are types of rodents. Rats are about ten times bigger and smarter than mice, so they are often used for surgery and brain or physiology research.
※3 Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A method where a sperm is directly injected into an egg using a very fine glass needle. This technique is also used in fertility treatments for humans.
Researchers
Name: Toshihiro Kobayashi, Mami Oikawa, Kenyu Iwatsuki, Hijiri Saito
Department: Division of Mammalian Embryology
Institute: The Institute of Medical Science, The University of Tokyo
Name: Hisato Kobayashi, Kazuki Kurimoto
Department: Department of Embryology
Institute: Nara Medical University
Name: Tomoyuki Yamaguchi
Department: Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine
Institute: Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Science
Name: Takuya Yamamoto
Department: Department of Life Science Frontiers
Institute: Center for iPS Cell Research and Application, Kyoto University
Journal
Title: Transcription factor-mediated germ cell induction in rats reveals ETV4 cooperates with germline specifiers
Authors: Mami Oikawa, Hiroki Kojima, Hisato Kobayashi, Kenyu Iwatsuki, Hijiri Saito, Makoto Sanbo, Kazumi Nishioka, Tomoyuki Yamaguchi, Takuya Yamamoto, Kazuki Kurimoto, Masumi Hirabayashi, Toshihiro Kobayashi
Journal: Stem Cell Reports
Issue: vol.20 102599
Date: August 12, 2025
URL (abstract): https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(25)00203-6
Grant
JSPS KAKENHI (23K20043, 24K01944, 25H01349)
AMED (JP22bm1123008)
JST (JPMJFR233J)
Daiichi Sankyo Foundation of Life Science
AMED (JP22bm1123008)
JST (JPMJFR233J)
Daiichi Sankyo Foundation of Life Science

