Survival of Corticostriatal Neurons by Rho/Rho-kinase Signaling Pathway
Developing cortical neurons undergo a number of sequential developmental events including neuronal survival/apoptosis, and the molecular mechanism underlying each characteristic process has been studied in detail. However, the survival pathway of cortical neurons at mature stages remains largely uninvestigated. We herein focused on mature corticostriatal neurons because of their important roles in various higher brain functions and the spectrum of neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders.
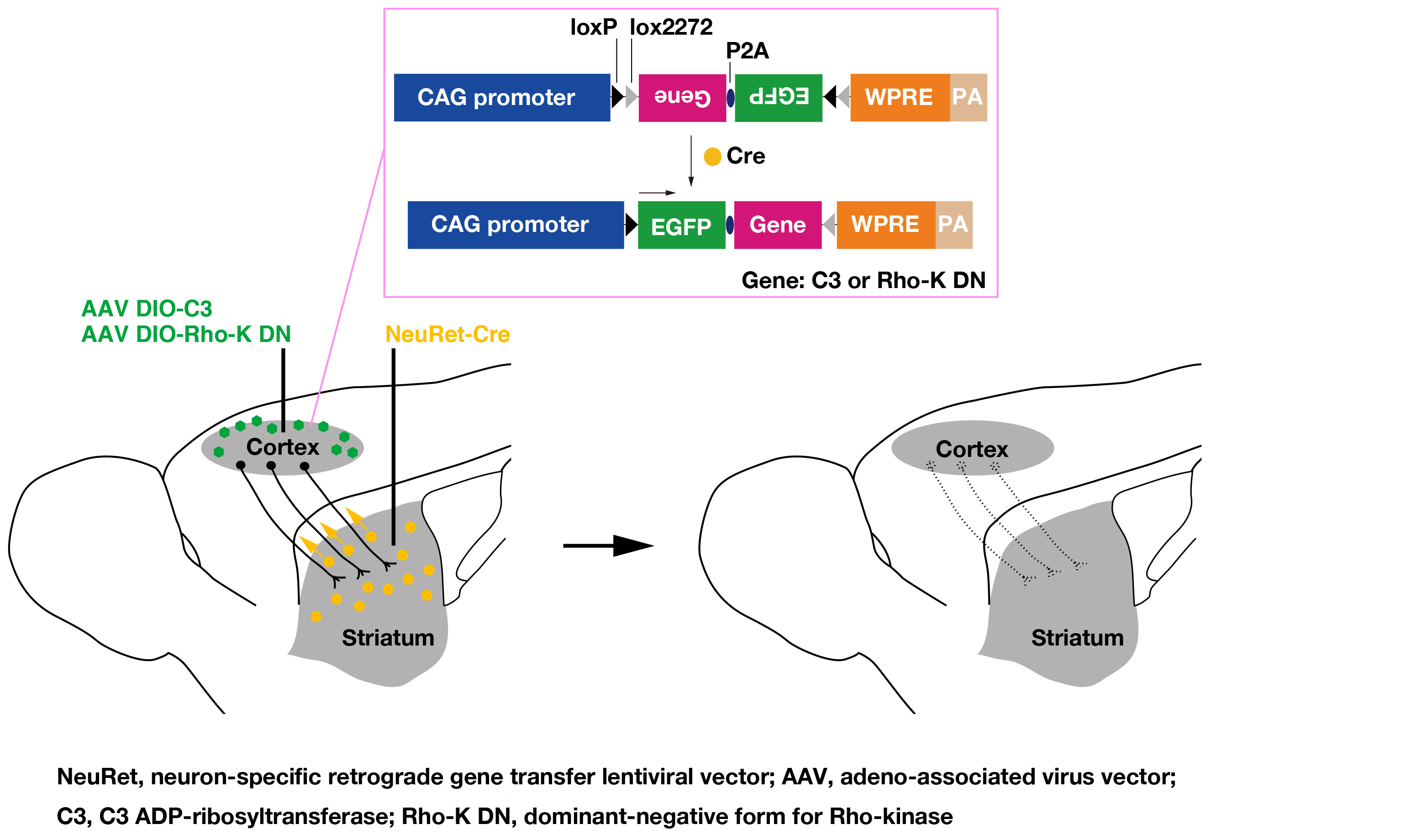
The small GTPase Rho is known to control diverse and essential cellular functions through some effector molecules, including Rho-kinase, during neural development. In the present study, we investigated the role of Rho signaling through Rho-kinase in the survival of corticostriatal neurons. We performed the conditional expression of Clostridium botulinum C3 ADP-ribosyltransferase (C3 transferase) or dominant-negative form for Rho-kinase (Rho-K DN), a well-known inhibitor of Rho or Rho-kinase, respectively, in corticostriatal neurons using a dual viral vector approach combining a neuron-specific retrograde gene transfer lentiviral vector and an adeno-associated virus vector.
C3 transferase markedly decreased the number of corticostriatal neurons, which was attributed to caspase-3-dependent enhanced apoptosis. In addition, Rho-K DN produced phenotypic defects similar to those caused by C3 transferase. These results indicate that the Rho/Rho-kinase signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the survival of corticostriatal neurons.
Collaborative Researcher
Shigeki Kato and Kazuto Kobayashi
Molecular Genetics, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Fukushima Medical University School of Medicine
Keisuke Kuroda, Shinichi Nakamuta, and Kozo Kaibuchi
Cell Pharmacology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine
Tadashi Isa
National Institute for Physiological Sciences and Kyoto University
Funding
Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Numbers 25560436, 25351002, and 15H01458. The Brain/MIND project from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED).

