Observation of composite microgels produced in the presence of water-swollen hydrogel microspheres by cryo-electron tomography
Composite microgels are soft materials like agar greatly swollen with water, but originally it consists of fine particles with a diameter of less than 1 μm (1/1000 of 1 mm). It is possible to change the characteristics of gel particles largely according to the external environment, for example, the size of fine particles will change about twice as the temperature changes. Since composite microgels are almost composed of water (about 90% or more), medicines, proteins, and pigments are confined in the microgels and released outside the gels at the intended place and at the intended time. It is expected to be applied as a drug delivery carrier in recent years. The research group of Dr. Suzuki in Shinshu University creates composite microgels with various shapes and functions in its own way and is conducting research on its application.
Composite microgels are normally dispersed in solution. In order to observe these microgels prepared by various methods, an electron microscope with higher resolution than the light microscope is required. However, since the sample must be placed in a vacuum, the exact shape of composite microgels cannot be directly observed. In this study, we rapidly frozen the composite microgels in solution and directly observed using a cryo-electron microscope installed in NIPS. Furthermore, we reconstructed its three-dimensional shape using a method called tomography. As a result, it was found that styrene forming composite microgels uniformly and largely polymerized inside the hydrogel microspheres negatively charged on the surface as the concentration of styrene was higher (see Figure). It became clear that styrene is incorporated into hydrogel microspheres and polymerized.
The results gave accurate information on the structure in solution necessary for designing composite microgels, such as drug delivery carriers.
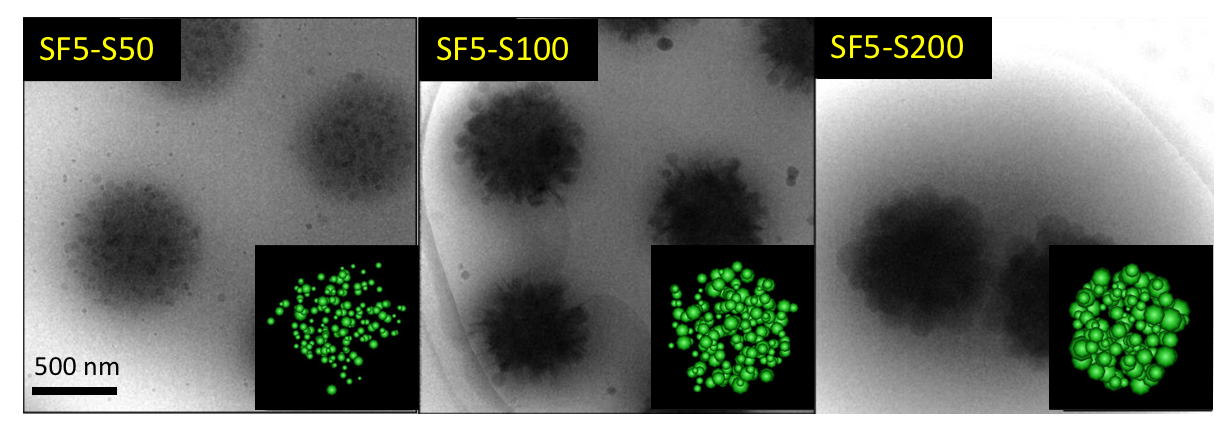
Figure Cryo-EM images of composite microgels and the tomographic 3D reconstructions (Inserted figures). Composite microgels (SF5-SX) are produced in the presence of hydrogel microspheres (SF5) with Styrene. X indicates the concentration of Styrene (50mM, 100mM, 200mM, respectively).
Collaborative Researcher
Takumi Watanabe, Daisuke Suzuki (Shinshu Univ.)
Funding
KAKENHI (Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas - and the Platforms for Advanced Technologies and Research Resources, “Advanced Bioimaging Support”)
Release Source
Title: Seeded Emulsion Polymerization of Styrene in the Presence of Water-Swollen Hydrogel Microspheres
Authors: Takumi Watanabe, Chihong Song, Kazuyoshi Murata, Takuma Kureha, and Daisuke Suzuki
Journal: Langmuir
Issue: 34(29), 8571
Date: 2018.6.29 publish & online
URL (abstract): https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01047
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01047

