Phosphoinositides modulate the voltage dependence of two-pore channel 3
Phosphoinositides are a series of important signaling lipids that are located in the cell membrane. They have variations in the locations that phosphates groups occupy (Fig. A). Each type of phosphoinositide evokes a different response to the cells. For example, PI(4,5)P2, in which two phosphate groups are located at the 4th and 5th positions, regulates the intracellular Ca2+ concentration, while PI(3,4)P2 is related to the morphological change of the plasma-membrane. Two-pore Na+ channels (TPCs) are the unique type of voltage-gated ion channels that can be modulated by both phosphoinositides and membrane voltage. Therefore, TPCs can integrate these two important signals. TPC family has three subtypes, and only TPC3 was believed to be insensitive to any phosphoinositides.
We found that TPC3 is also sensitive to the specific phosphoinositides, as well as TPC1 and TPC2. Intriguingly, TPC3 showed the PI(3,4)P2 sensitivity, while TPC1 and TPC2 selectively respond to PI(3,5)P2. The PI(3,4)P2 binding to TPC3 modulates its voltage dependence, which is unique among TPC family. We revealed the structural basis for these unique features of TPC3, PI(3,4)P2-dependent modulation of the voltage-dependence, using the TPC3 model structure and mutagenesis analyses (Fig. B). Our study will contribute to the understandings of the phosphoinositide recognition mechanism in not only TPC family, but also general ion channels.
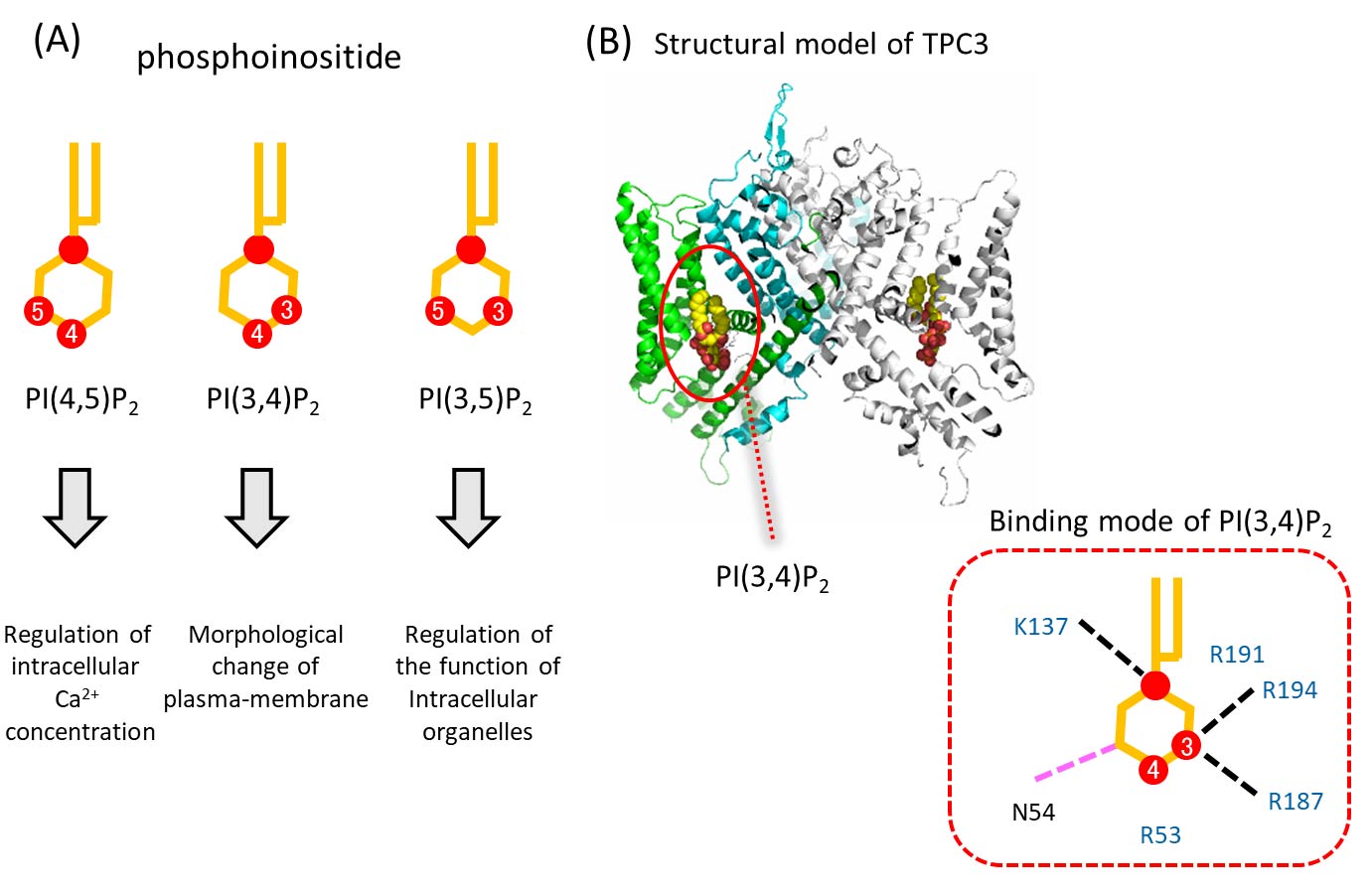
phosphoinositides and TPC3
(A) A cartoon of the phosphoinositides. (B) The structural model of TPC3 and the detailed binding mode of PI(3,4)P2 in TPC3.
*An illustration explaining the research contents was adopted as a cover of the published issue (Journal of General Physiology (2019) 151(8)).
Funding
This work was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research<KAKENHI>
Release Source
Title: Phosphoinositides modulate the voltage dependence of two-pore channel 3
Authors: Takushi Shimomura and Yoshihiro Kubo
Journal: Journal of General Physiology
Date: 2019 Jun 10
URL (abstract): http://jgp.rupress.org/content/early/2019/06/07/jgp.201812285
DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201812285

