Localization of the protein that controls ciliary movement by light
Cilia are responsible for sperm swimming, the fluid flow on the bronchial surface, and many other important features of cell motility. Deficiency of the proteins that build cilia causes various ciliopathies including infertility. The movement of cilia is caused by the motor activity of a protein called "dynein" on the microtubules using the energy of ATP.
Recently, research groups of Professor Kazuo Inaba at the University of Tsukuba and Professor Takahide Kon and Assistant Professor Hiroshi Imai at Osaka University discovered a new subunit of dynein in cilia. Deficiency of this subunit named "DYBLUP (dynein-associated BLUF protein)" was shown to cause abnormal regulation of ciliary movement in response to light.
In this joint research, we investigated where DYBLUP is located and what its function is in cilia by structural analysis using cryo-electron tomography. As a result, it was found that DYBLUP forms a part of the structure called “tether” that connects dynein and microtubule. It was also revealed that DYBLUP regulates the function of the tether in response to blue light.
In this study, we clarified the mechanism how the movement of cilia is regulated by light. Our study not only clarified the molecular mechanism of a part of photoresponses in organisms (phototaxis, etc.), but also suggests the possibility of light-induced manipulation of cell motility in the future.
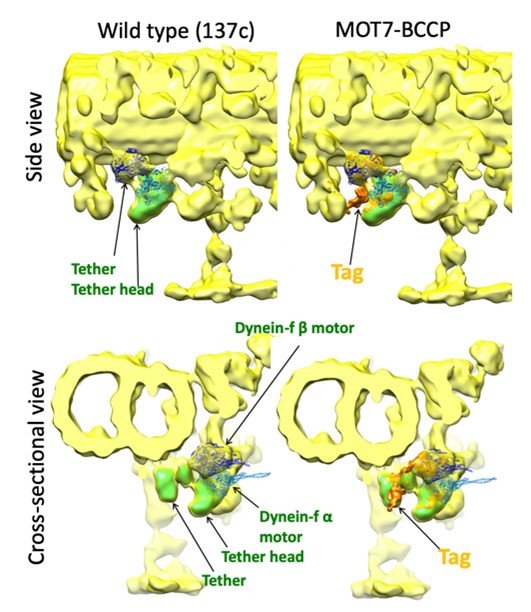
Structures of the wild type cilia (left) and the mutant cilia labeled DYBLUP (right)
Collaborative Researcher
Hiroshi Imai, Ryosuke Yamamoto, Takahide Kon (Osaka University)
Kazuo Inaba (The University of Tsukuba)
Chihong Song, Kazuyoshi Murata (NIPS)
Funding
Collaborative Study Program of NIPS
Release Source
Title: A dynein-associated photoreceptor protein prevents ciliary acclimation to blue light
Authors: Osamu Kutomi, Ryosuke Yamamot, Keiko Hirose, Katsutoshi Mizuno, Yuuhei Nakagiri, Hiroshi Imai, Akira Noga, Jagan Mohan Obbineni, Noemi Zimmermann,
Masako Nakajima, Daisuke Shibata, Misa Shibata, Kogiku Shiba, Masaki Kita, Hideo Kigoshi, Yui Tanaka, Yuya Yamasaki, Yuma Asahina, Chihong Song, Mami Nomura, Mamoru Nomura, Ayako Nakajima, Mia Nakachi, Lixy Yamada, Shiori Nakazawa, Hitoshi Sawada, Kazuyoshi Murata, Kaoru Mitsuoka, Takashi Ishikawa, Ken-ichi Wakabayashi, Takahide Kon, Kazuo Inaba
Journal: Science Advances
Issue: Vol. 7, eabf3621
Date: 26 February, 2021
URL: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/7/9/eabf3621

